Refrigeration plants are crucial in various industries, from food production to pharmaceutical manufacturing. However, operating these plants involves various inherent risks, particularly when using ammonia as a refrigerant. Ensuring safety within these environments is a matter of regulatory compliance and a commitment to protecting the lives of workers and the integrity of your business operations.
One of the key components in maintaining a safe refrigeration plant is using ammonia gas detectors. These devices monitor ammonia levels in the air and alert personnel when the concentration reaches an unsafe level. They serve as the first line of defense against potential ammonia leaks, which can harm human health and the environment. Learn more about the importance of ammonia gas detectors in refrigeration plants.
Understanding Ammonia and Its Uses in Refrigeration
Ammonia, a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3, is a colorless gas with a characteristically pungent smell. It occurs naturally in the environment from the breakdown of organic waste matter and is a byproduct of many industrial processes. Ammonia has a boiling point of -33.34 degrees Celsius in its pure form, so it can liquefy under pressure without extreme cooling.
Ammonia serves as an effective refrigerant due to its unique physical properties. It possesses a high heat capacity, which means it can absorb a large amount of heat from the environment. This characteristic makes it ideal for use in systems designed to lower temperatures and maintain them at a desired level. Furthermore, ammonia’s low boiling point allows it to evaporate quickly, absorbing heat in the process and creating a cooling effect. Using ammonia as a refrigerant offers several benefits. It’s highly energy-efficient, reducing the operational costs of refrigeration systems. Moreover, unlike many other refrigerants, ammonia doesn’t contribute to ozone layer depletion or global warming. This makes it an environmentally friendly choice.
Health and Safety Hazards Associated With Ammonia
Exposure to high concentrations of ammonia can cause harm to the human body, leading to eye irritation, respiratory problems, and, in severe cases, death. In severe cases, exposure can result in blindness or life-threatening pulmonary edema, a condition where fluid accumulates in the lungs. Additionally, ammonia can react with other substances to form explosive mixtures in certain conditions.
However, the most concerning situation is long-term ammonia exposure, which leads to many health complications. Repeated exposure to ammonia can exacerbate chronic respiratory conditions like bronchitis and asthma. Additionally, prolonged contact with the skin can cause burns and irritations. Therefore, workers in refrigeration plants and other facilities using ammonia must take preventative measures to limit exposure. Ammonia also presents safety hazards to structures and equipment. As a corrosive substance, it can damage materials like copper, zinc, and many alloys. This corrosion can lead to equipment failure and costly repairs. Moreover, if ammonia leaks into the environment, it can harm local ecosystems, affecting both plant and animal life.
Lastly, under certain conditions, ammonia can pose a risk of fire or explosion. While it’s not highly flammable, an ammonia leak in an enclosed space can create an explosive mixture if there’s a source of ignition present. This makes the management of ammonia in refrigeration plants important. Any plant needs a reliable detection system to prevent leaks and ensure the safety of personnel and infrastructure.
What To Know About Ammonia Gas Detectors
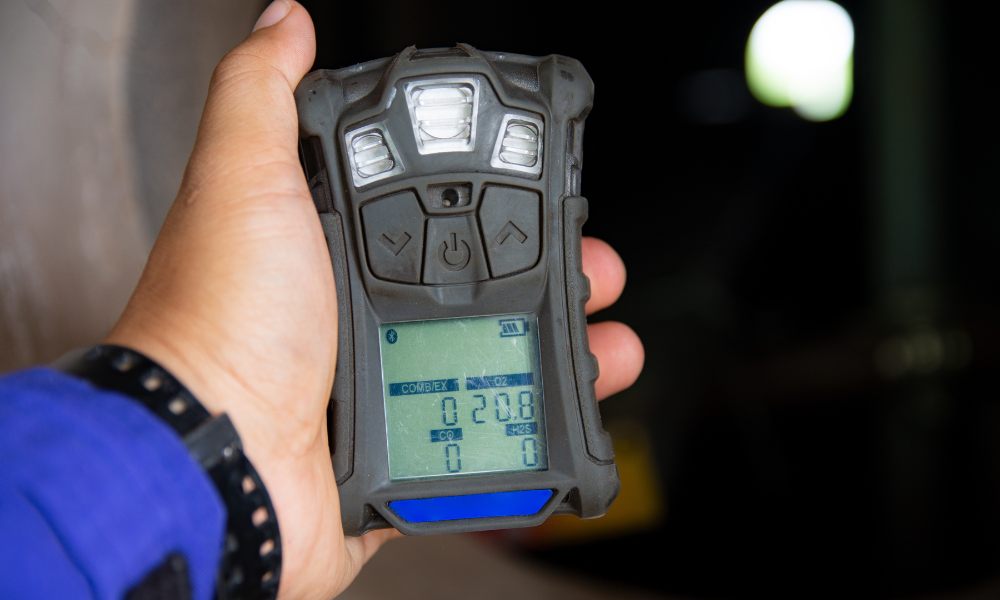
Now that you know more about the characteristics and hazards of ammonia, you must understand ammonia gas detectors. An ammonia detector functions by identifying ammonia’s presence in the air and measuring its concentration. It does this through a sensor that reacts to ammonia on a chemical level. When the gas comes into contact with the sensor, it triggers a reaction that generates an electrical signal. The detector’s system then processes and interprets this signal to provide a reading of the ammonia level in the environment. If the concentration exceeds a predetermined safe level, the detector activates an alarm to alert personnel of the potential hazard.
There are two main types of ammonia gas detectors: fixed and portable. Fixed ammonia gas detectors serve a crucial function in areas with a heightened risk of ammonia leakage, such as industrial refrigeration plants. These detectors are in static locations to monitor the surrounding environment continuously. They vigilantly scan for the presence of ammonia, providing constant surveillance of the air quality.
In addition to their primary installation points, plants often have fixed detectors in problematic areas that require additional monitoring. These might be locations where leaks have occurred in the past or areas housing equipment susceptible to ammonia damage. The strategic placement of these detectors allows for thorough coverage and robust safety measures, ensuring the well-being of both the workforce and the facility’s infrastructure.
On the other hand, many plants employ handheld portable detectors to monitor ammonia levels in specific locations. Safety officers or technicians often use them during routine checks or when investigating potential leaks. These devices offer flexibility and mobility, allowing for quick and efficient identification of hazardous zones within a facility. Whether using fixed or portable detectors, choose a device that meets the facility’s specific needs.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Device for Your Plant
Several factors demand careful attention when choosing the right monitoring device for your plant. First, consider the specific requirements of your facility, including the types of gases present and their expected concentration levels. The detector you choose should have the capacity to measure these levels accurately. Secondly, evaluate the environmental conditions within your plant. Extreme temperatures, humidity, and dust can impact a detector’s performance; select a device designed to withstand your facility’s conditions. Lastly, consider the ease of use and maintenance. A user-friendly device with straightforward maintenance procedures can save significant time and resources.
Selecting a reliable monitor manufacturer and supplier is equally as important as choosing the right device. A credible manufacturer ensures the detectors’ quality, accuracy, and durability. They often provide comprehensive technical support and warranty services, which can prove invaluable over the device’s lifespan. Similarly, a dependable supplier can offer valuable advice on selecting the most suitable device for your needs. They can provide ongoing support, including regular maintenance and calibration services, ensuring your detectors continue to operate effectively.
Thankfully, our Calibration Technology team boasts all these characteristics and more! Contact our friendly team today and learn more about our industry-leading selection of ammonia and related gas detection devices. You can ensure superior safety and productivity by understanding the importance of ammonia gas detectors in refrigeration plants and equipping your facility with quality equipment.